As an experienced cannabis grower, I’ve learned the importance of mobile and immobile nutrients in nurturing thriving plants, especially cannabis plants.
Mobile nutrients freely move within the plant, fueling growth and enhancing flower development. On the other hand, immobile nutrients remain rooted in different parts of plants where they were absorbed. These nutrients provide stability, activate vital enzymes, and participate in chlorophyll synthesis (the core process for plant development).
Understanding the difference between these nutrient types will empower you to diagnose deficiencies and provide targeted nourishment.
So, my fellow cultivators, let’s dive deep into the details of mobile and immobile nutrients. Harness this knowledge to become a nurturing guardian for your plants, understanding the precise elements they require.
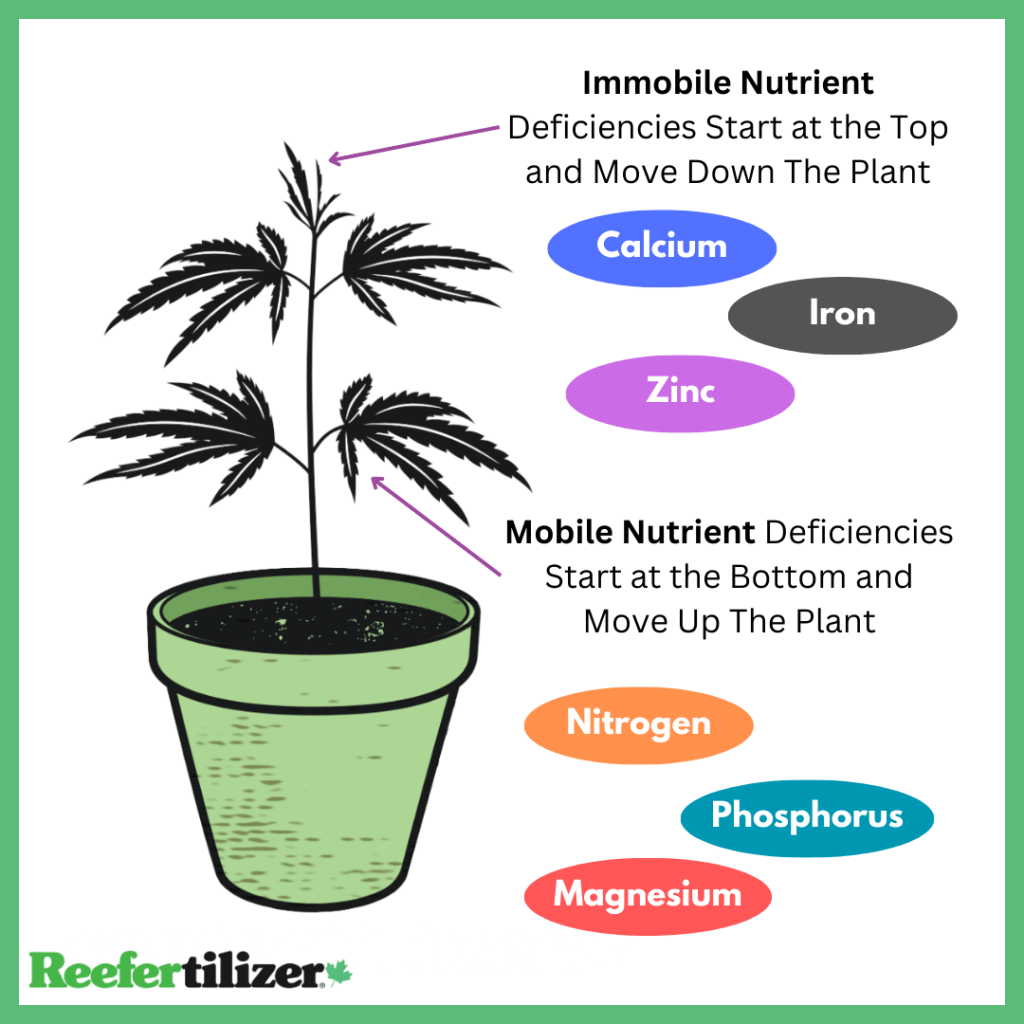
Long story short; mobile nutrient deficiencies show symptoms on lower leaves and move up the plant. Immobile deficiencies show symptoms on new growth. Use this to help narrow down what type of nutrient deficiency your plant might be suffering from.
Be sure to rule out pH and soil problems before diagnosing a nutrient deficiency.
Mobile Nutrients
Mobile nutrients are essential elements required for the growth and development of plants that easily move within the plant. Examples of mobile nutrients is includes Nitrogen, Phosphorus, potassium and others.
Mobile nutrients can move freely within the plant’s vascular system. The plant’s vascular system is a transport mechanism that links all the plant’s organs together and carries water, minerals, nutrients, and organic substances throughout the entire plant structure.
Immobile Nutrients
Immobile nutrients are essential elements required for the growth and development of plants that cannot move freely inside the plant once they have been absorbed. These nutrients are mainly absorbed by the roots and remain fixed in the tissues where they were initially taken up.
They are unable to move freely to other parts of the plant, such as from old leaves to new leaves or from older to younger tissues. As a result, the availability of immobile nutrients is crucial in the areas where they are initially deposited.
Mobile Nutrients & their Functions
Nitrogen (N) Nitrogen is essential for plants because it helps them grow strong and healthy. It is a key component of proteins, which are important for building cells and tissues. Nitrogen also helps plants produce chlorophyll, the green pigment that enables them to carry out photosynthesis and make food. Without enough nitrogen, plants may become weak, have stunted growth, or have yellowing leaves. |
Phosphorus (P) Phosphorus plays a vital role in energy transfer and storage within the plant. It is involved in processes like photosynthesis, and respiration. Phosphorus can be transported from older tissues to areas of active growth, such as root tips and developing leaves. |
Potassium (K) Potassium is another important nutrient for plants. It helps them in many ways. First, it helps regulate water balance within plant cells, ensuring they don’t become too dry or too swollen. Potassium also plays a vital role in the activation of enzymes, which are like tiny workers inside plants that help with various processes. Additionally, potassium helps plants build strong roots and stems, making them more resistant to diseases and pests. |
Magnesium (Mg) Plants need magnesium to make food and stay healthy. It helps them use sunlight effectively, grow green leaves, and carry out important functions. Magnesium is like a special nutrient that plants require to thrive and stay strong. |
Immobile Nutrient and their functions
Calcium (Ca) Calcium is a vital nutrient for plants as it contributes to the strength and structure of cell walls in plants, making them sturdy. Secondly, calcium is important for cell division and growth, promoting healthy root and shoot development. |
Sulfur (S) Sulfur has many functions in plants such as growth and development. Firstly, sulfur is a component of certain amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. This means sulfur is necessary for plants to produce proteins, which are crucial for cell structure and function. Secondly, sulfur is involved in the synthesis of vitamins in plants. It also plays a role in the formation of chlorophyll, the green pigment responsible for photosynthesis. |
Boron (B) Boron is a vital nutrient for plants. Even though it is needed in small amounts, it plays a significant role in plant growth and development. Firstly, boron is essential for cell wall formation, which provides structural support to plants. It also influences the transport and utilization of sugars within the plant. Additionally, boron is involved in pollen development and germination, helping with successful reproduction in flowering plants. It is crucial for flowering, and seed development in cannabis plants. |
Iron (Fe) Plants need iron to grow and stay healthy. It helps them make food by capturing sunlight. Iron is like a special ingredient that plants use to create a green pigment called chlorophyll, which helps them make energy. Iron also helps plants with important jobs like taking in nutrients, making DNA, and producing hormones. It’s like a superhero nutrient that helps plants grow, make food, and do important things to stay strong and healthy. |
Zinc (Zn) First, zinc is necessary for the production of enzymes, which are like little helpers that carry out important tasks in plants. These enzymes help with processes like making proteins and breaking down sugars. Zinc also helps plants develop strong roots and helps them grow and reproduce. Additionally, zinc plays a role in plant defense mechanisms, helping them fight off diseases and pests. Zinc deficiency can cause stunted growth, distorted leaves, and delayed flowering. |
Diagnosing Nutrient Deficiencies
Visual signs and symptoms of mobile nutrient deficiencies
Plants communicate their nutrient needs through visual cues. When mobile nutrients are lacking, specific signs and symptoms appear, primarily in the older leaves. Here is what I noted:
- Yellowing or discoloration starting from the bottom leaves and progressing upwards.
- Stunted growth and reduced leaf size.
- Leaves turning pale or showing interveinal chlorosis (yellowing between leaf veins).
- Premature leaf drop or leaf death.
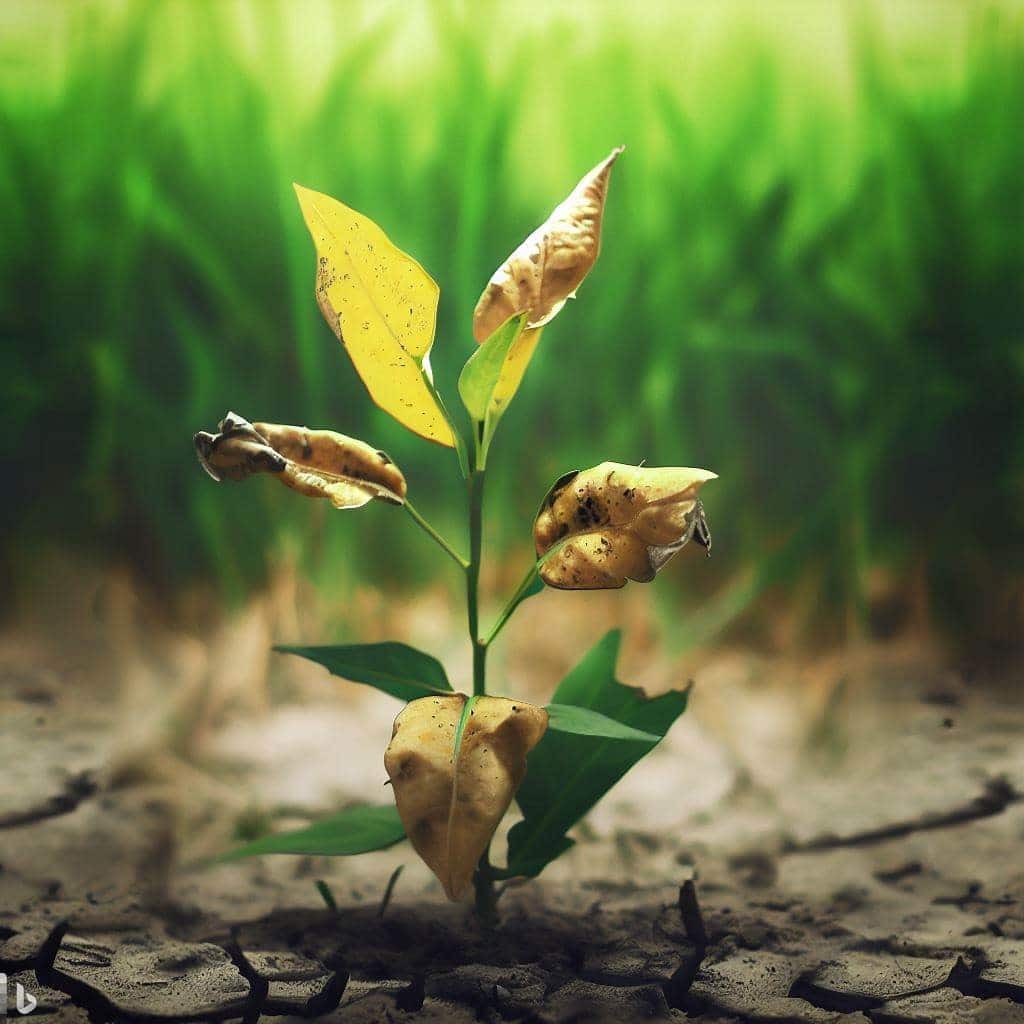

Visual signs and symptoms of immobile nutrient deficiencies
Immobile nutrient deficiencies often affect the newer leaves. Look for the following signs to identify potential immobile nutrient deficiencies:
- Interveinal chlorosis, where the leaf veins remain green while the spaces between them turn yellow or show discoloration.
- Browning at leaf edges.
- Distorted or twisted leaf growth.
- Slowed growth and smaller leaf size in the affected areas.
How to identify nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants?
To identify nutrient deficiencies accurately, I suggest you observe the overall health and appearance of your cannabis plants. Regularly inspect them for any signs of stress or abnormal growth. You may consider the following steps for a thorough assessment:
- Visual inspection: Observe the leaves, stems, and overall plant structure for any discoloration, spots, wilting, or unusual growth patterns.
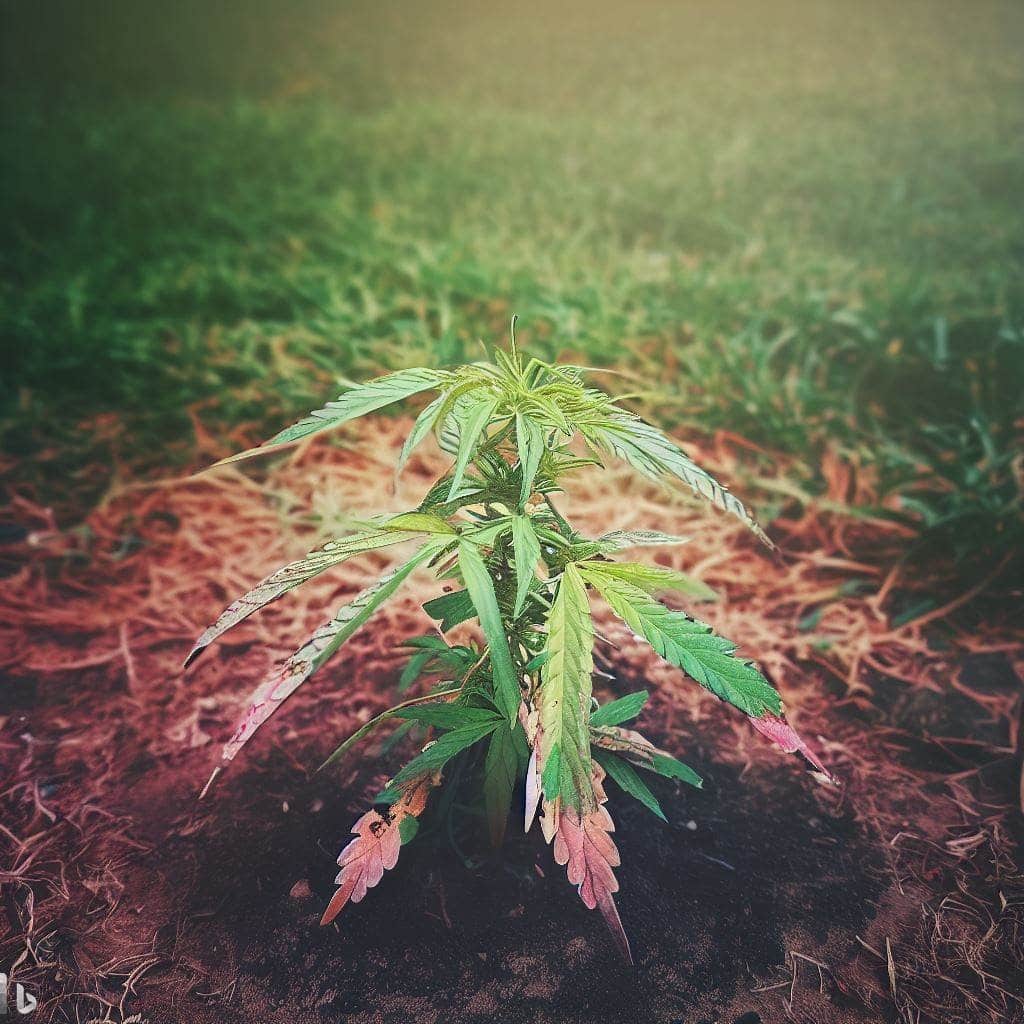

- Compare leaf symptoms: Compare the symptoms you observe with a nutrient deficiency chart or guide specific to cannabis plants to help narrow down potential deficiencies.
- Consider the growth stage: Nutrient needs may vary depending on the growth stage of your plants. Take into account whether they are in the vegetative or flowering phase, as nutrient requirements may differ.
- Evaluate growing conditions: Assess factors such as pH levels, water quality, light intensity, and temperature, as these can affect nutrient uptake and availability.
- Keep a record: Maintain a journal or take pictures to track changes in symptoms and plant response to nutrient adjustments.
When it comes to nurturing your cannabis plants with the right nutrients, Reefertilizer is a trusted name in the industry. We offer a range of high-quality products designed to meet the specific needs of cannabis cultivation. You can explore plant nutrient offerings and how they can benefit your plants.
Reefertilizer Cannabis Nutrients
At Reefertilizer we understand the unique requirements of cannabis plants throughout their growth cycle. Our nutrients are carefully formulated to provide the essential elements needed for healthy and robust plant development at each stage of growth.
Here’s how Reefertilizers’ products address the needs of your cannabis plants:

- Balanced nutrient ratios: Our nutrient formulas are crafted to provide the optimal balance of macro and micronutrients. This ensures that your cannabis plants receive a comprehensive nutrient profile, supporting their overall growth and vitality.
- Highly bioavailable ingredients: We source top-quality ingredients that are easily absorbed by plants. This ensures efficient nutrient uptake and minimizes the risk of nutrient deficiencies, allowing your cannabis plants to thrive.
- Tailored formulations for growth stages: We offer specific nutrient blends for different growth stages of cannabis plants, such as the vegetative and flowering phases. These formulations address the changing nutrient requirements of your plants, maximizing their potential during each stage of growth.
Grow Better Weed with Mobile and Immobile Nutrients
Understanding the difference between mobile and immobile nutrients is very important for diagnosing and addressing nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants. By recognizing the visual signs and symptoms, utilizing soil and tissue testing, and incorporating the right nutrient products, we can optimize the growth and health of our plants.
Reefertilizers, with their carefully formulated nutrient offerings, provide a reliable solution for cannabis growers. Whether you’re cultivating a single plant or a small-scale operation, Reefertilizers’ products are designed to meet the unique needs of cannabis cultivation.
If you want to learn even more about growing good cannabis, we offer a free 40+ page guide full of images.
Now available on Amazon.
Sign up for our newsletter and download the digital copy today!

This guide will answer many questions about growing cannabis, like the following...
Selecting Seeds
Identify and Correct Problems
Maximize Yield
Much More...
Get a Chance to INSTANTLY WIN a Reefertilizer Nutrient Kit When You Sign Up.

Mike Drouin is the co-founder of Reefertilizer. He’s an experienced craft cannabis grower and a writer of many articles regarding the process. Mike lives on Vancouver Island and enjoys cycling and camping and will sometimes combine the two.
