Explore the key compounds that shape your cannabis experience. From cannabinoids like THC and CBD to fragrant terpenes like limonene and pinene, each plays a crucial role in the effects of different strains.
Learn to Grow Better Weed
Download our free guide to growing amazing cannabis at home.
Click Here For More Info
Cannabinoids
These active compounds found in cannabis plants tap into the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), which plays a vital part in maintaining internal balance. They can affect various physiological and cognitive processes, including mood regulation, pain management, hunger signals, and memory. There are over 100 different cannabinoids, with THC and CBD being the most recognized. Each interacts with ECS receptors, primarily CB1 and CB2, in different ways and can support the body in maintaining overall wellbeing.
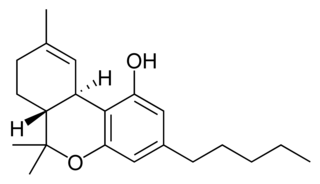

THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
Recognized as the most prominent psychoactive component in cannabis, THC is what typically brings about the feeling of euphoria associated with cannabis use. When consumed, THC binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and throughout the body, which can result in a range of effects including heightened senses, altered perception of time, and increased appetite. While many users appreciate THC’s potential in managing discomfort and reducing nausea, particularly in therapeutic contexts, it’s also known that it may increase feelings of unease or nervousness in certain individuals. Its complexity is augmented by potential therapeutic benefits, such as its neuroprotective properties and ability to prompt cell death in certain types of cancer cells, though these areas are still under scientific investigation.
CBN (Cannabinol)
This cannabinoid emerges when THC, the active psychoactive chemical in cannabis, breaks down over time and comes into contact with oxygen. Unlike THC, CBN is considerably less psychoactive, which means it doesn’t make you feel as high. It’s of significant interest to researchers due to its potential to aid with sleep and provide a tranquilizing effect on the body, making it a subject of study for those with sleep disorders. Moreover, CBN might have anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving qualities, thereby offering a range of possible therapeutic applications. Even though it’s not as well-known as CBD or THC, CBN’s emerging profile as a milder, sleep-friendly compound is gaining attention within the cannabis community and among those exploring alternative remedies for relaxation and rest.
THC-A (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid)
THC-A is essentially the precursor to THC, the compound responsible for the psychoactive effects typically associated with cannabis. In its raw form, THC-A is not active, meaning it won’t induce a high when consumed. This is due to its chemical structure, which includes an extra carboxyl group that prevents it from effectively binding with CB1 receptors in the brain.
It’s only when heated—through smoking, vaping, or cooking, for instance—that THC-A undergoes the transformation into THC. This chemical reaction, known as decarboxylation, removes that extra carboxyl group, activating the compound. Aside from its role as a precursor to THC, THC-A is an interesting substance in its own right and is being researched for potential therapeutic properties, such as its anti-inflammatory effects. As it exists in fresh cannabis leaves and flowers, THC-A also becomes a point of interest for individuals who are looking into the medical benefits of cannabis without the high.
Delta-9-THC
Delta-9-THC is the primary form of tetrahydrocannabinol, the compound in cannabis renowned for its strong psychoactive properties. When you enjoy cannabis, it’s mainly the Delta-9-THC that is responsible for the classic effects such as changes in perception, heightened mood, and the altered sense of time that many people experience.
This compound functions by interacting with the body’s endocannabinoid system, specifically binding to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and nervous system. The significant presence of Delta-9-THC in cannabis varies but can be as high as 30% by weight in some strains.
When consumed, Delta-9-THC can have various impacts on an individual’s mental state, potentially providing sensations of euphoria and relaxation. However, sensitivity to Delta-9-THC’s effects can vary, and in some cases, it may lead to less comfortable experiences such as anxiety or paranoia.
Research into Delta-9-THC has also uncovered potential therapeutic uses, such as aiding those with chronic pain, improving appetite in people with medical conditions that suppress hunger, and offering relief to patients undergoing chemotherapy by reducing nausea and vomiting.
While its medical benefits continue to be explored, Delta-9-THC remains a controlled substance in many parts of the world, with legality varying greatly from one region to another.
Delta-8-THC
Delta-8-THC is akin to Delta-9-THC’s less potent sibling, providing a more subdued version of the psychoactive experience. Users often report that it delivers calming and soothing effects without the intensity usually associated with Delta-9-THC. This cannabinoid engages with the endocannabinoid system’s CB1 and CB2 receptors, similar to Delta-9-THC, but its interaction is less powerful, often resulting in a clearer-headed experience.
Its presence in cannabis plants is minimal, typically less than 1%, which means it isn’t abundant naturally and often requires extraction and concentration to be used effectively. People might choose Delta-8-THC when they’re looking for a milder, less overwhelming encounter with THC’s effects or when they are interested in the potential therapeutic properties without a strong high.
Legally, Delta-8-THC sits in a complex space. Its status can vary significantly from place to place, making it important for consumers to research and understand their local laws before obtaining and using it. This legal ambiguity is also a factor that influences its availability and use.


CBD (Cannabidiol)
CBD is a key compound found in cannabis plants. Unlike THC, CBD does not make you feel high. It’s picked up a lot of interest for its potential to help with various health issues.
People are looking into how CBD might be able to calm your nerves and help you relax. It might also reduce soreness and swelling in the body. This has made it a popular choice for individuals who are seeking relief from various conditions but want to avoid the psychoactive effects of THC.
CBD can be found in high amounts especially in hemp plants. In places where cannabis is heavily regulated, products with CBD are often allowed as long as they have very little THC in them.
Terpenes
Terpenes are like the natural scents and flavors in cannabis. They help make each strain smell and taste different, like how some plants smell like lemons and others like pine trees. These compounds can also influence how you feel after using cannabis, making the experience more than just about THC or CBD. While terpenes are a small part of what’s in cannabis, they play a big role in making each strain unique.
Limonene
Limonene is found in the peels of citrus fruits and in cannabis. It’s known for its fresh, bright citrus aroma. People often associate it with uplifting effects and it may also help in reducing stress. Additionally, limonene has properties that can fight fungus and bacteria which are beneficial for both the plant and potentially for human use. It’s not only about the scent; it could also have a role in improving wellbeing.


Myrcene
Myrcene is a notable terpene in cannabis, abundant in many strains. It carries a distinct musky and earthy aroma that can deepen the scent profile of cannabis. This terpene is thought to encourage feelings of ease and might assist with sleep. Myrcene could potentially enhance the effects of THC, potentially leading to a more pronounced sense of calmness.
Pinene
Pinene is a common terpene in cannabis and smells similar to a forest of pine trees. It is known for its potential to help with memory and keeping you alert. Pinene also might help reduce inflammation, offering additional wellness benefits.
Entourage Effect
The entourage effect is a theory that suggests the compounds in cannabis, like cannabinoids and terpenes, work better when taken together. This means you might get more relief or benefit from cannabis because the different parts boost each other’s effects. This concept is why some people believe whole-plant cannabis products are more effective than just isolated parts like THC or CBD alone.
If you want to learn even more about growing good cannabis, we offer a free 40+ page guide full of images.
Now available on Amazon.
Sign up for our newsletter and download the digital copy today!


This guide will answer many questions about growing cannabis, like the following...
Selecting Seeds
Identify and Correct Problems
Maximize Yield
Much More...
Get a Chance to INSTANTLY WIN a Reefertilizer Nutrient Kit When You Sign Up.


Mike Drouin is the co-founder of Reefertilizer. He’s an experienced craft cannabis grower and a writer of many articles regarding the process. Mike lives on Vancouver Island and enjoys cycling and camping and will sometimes combine the two.

